Working with Arrays
What are Arrays?
We've used lots of Variables over the past few chapters. Each Variable holds a Value.
Wouldn't it be great if we could place lots of information into a single Variable, though?
That's where Arrays come in.
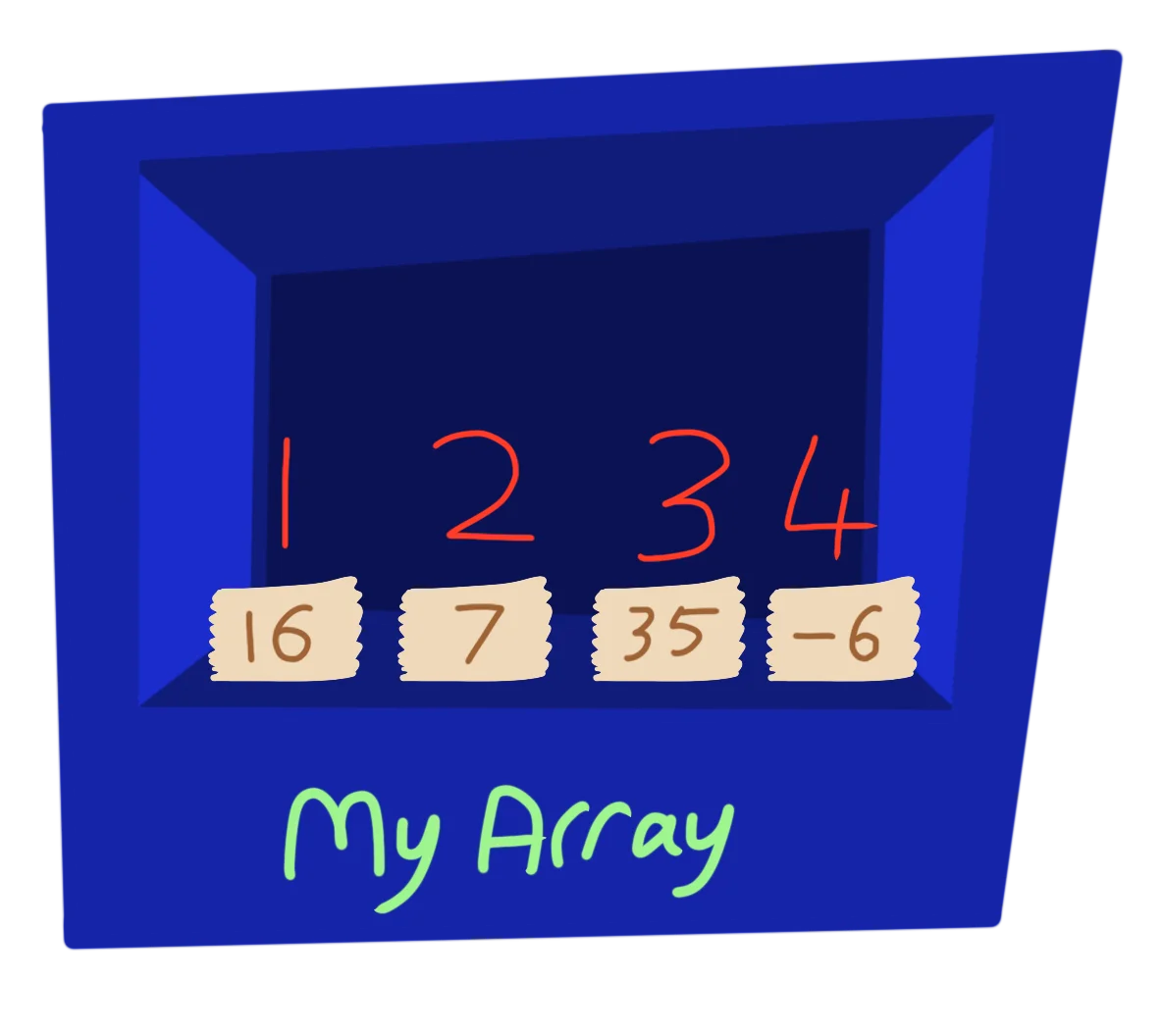
One box, many Values!
Instead of a Variable having one Value, and Array can have lots of Values.
We simply give it a slot number, and the Array lets us access that particular Value.
Using an Array
// Set up our array
Dim MyArray(4)
// Place Values into each slot
MyArray(1)=16
MyArray(2)=7
MyArray(3)=35
MyArray(4)=-6
// Access the Values in any order
Print MyArray(3)
Print MyArray(1)
Print MyArray(4)
Print MyArray(2)
First we need to create the Array. We use the Dim command to let the computer know what size of a box we'll need.
The name of the array is given, along with how many slot of Values we need inside the array.
To access and store Values in these slots, we then only need to give a slot number inside the brackets.

We can print the array in any order we like!
Just be sure that you've given the Array enough slots, or you'll run out!
Multiple Arrays
Just like with Variables, we can create lots of Arrays within our program.
Be sure to give each Array a recognisable name, so that you know what each one is for.
// Create a Name Array with 4 elements
Dim Name(4)
// Create an Age Array with 4 elements
Dim Age(4)
Name(1)="Dave"
Age(1)=7
Name(2)="Ted"
Age(2)=12
Name(3)="Bob"
Age(3)=10
Name(4)="Mr Green"
Age(4)=45
For J=1 To 4
Print Name(J)+" is "+Age(J)
Next
Multi-Dimensional!
As well as single slots all in a row, we can create two dimensional arrays!!
If we did a Dim MyArray(4,4), you can imagine it like being 4 rows, and each row has 4 slots.
Now you can jump to any of the 16 slots inside the 4x4 grid using MyArray(X,Y) to navigate the array.
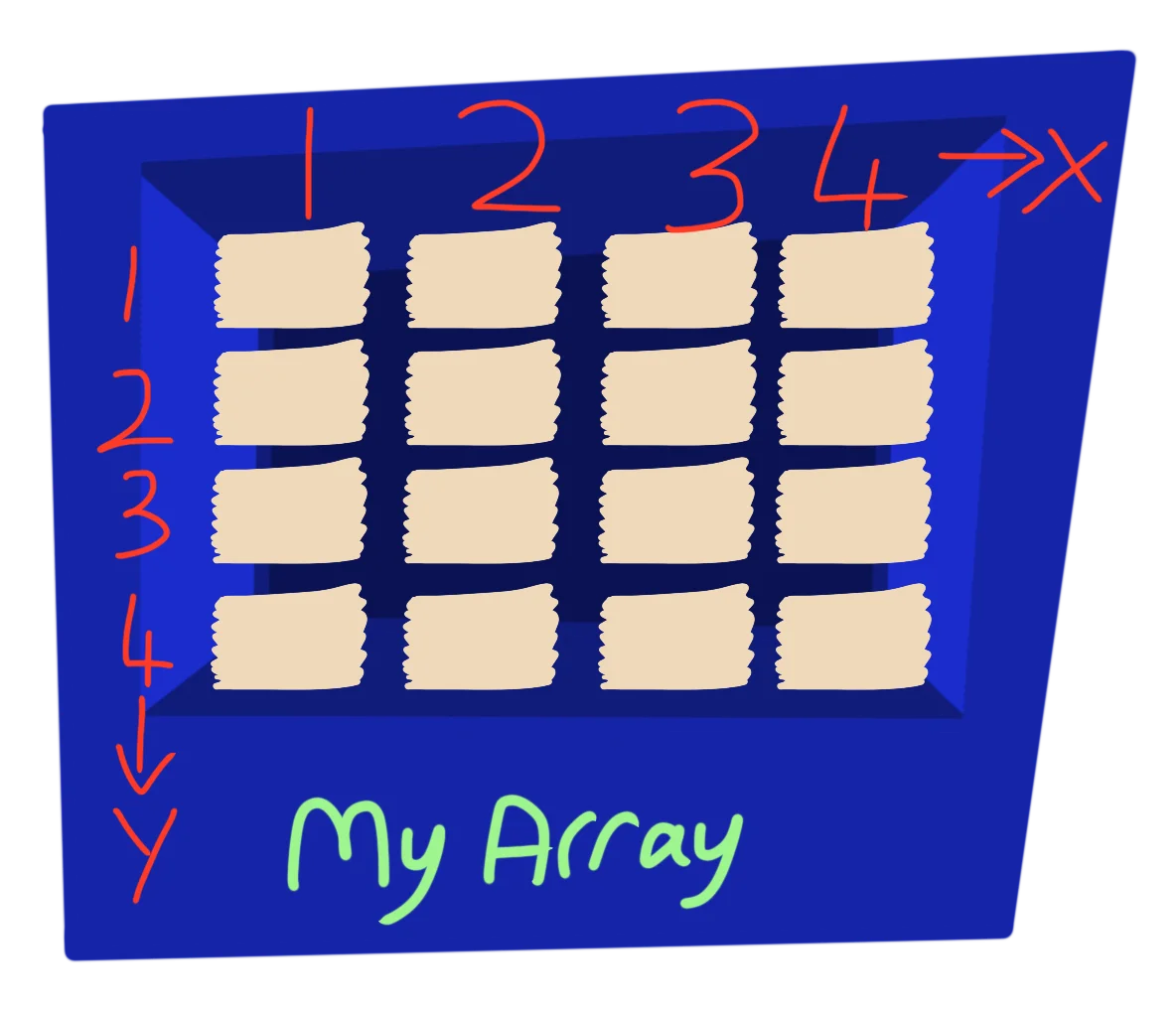
The array goes in two directions!
We can store even more information in it.
Practical Uses
Since we can store any values into an Array, we can make use of a Multi-Dimensional array to hold sets of values together.
Let's take our Name, Age example from earlier.
We can create a Multi-Dimensional array to hold both sets of information together.
// Set up a Multi-Dimensional Array
Dim ID(4,2)
// Give the two end slots different names
Name=1
Age=2
// Place the information into our Array
// giving each User their own Row in the Array.
ID(1,Name)="Dave"
ID(1,Age)=7
ID(2,Name)="Ted"
ID(2,Age)=12
ID(3,Name)="Bob"
ID(3,Age)=10
ID(4,Name)="Mr Green"
ID(4,Age)=45
For User=1 To 4
Print ID(User,Name)+" is "+ID(User,Age)
Next
Now each User has a Name and Age, and it's all inside our single Array.
Sorted!
We can also perform additional functions on Arrays.
There's SortArray, which will sort the array based on the value of the first column of each row.
Dim MyArray(10)
For J=1 to 10
MyArray(J)=Rand(0,100)
Print MyArray(J)
Next
Print
SortArray(MyArray)
For J=1 to 10
Print MyArray(J)
Next

The array is sorted.
There's also ReverseArray and ShuffleArray, which will perform similar tasks.
Sort the names!
Dim Name(5)
Name(1)="Joe"
Name(2)="James"
Name(3)="Jack"
Name(4)="Jill"
Name(5)="Jeff"
Print "The names in alphabetical order"
For J=1 to 5
Print Name(J)
Next
There are two ways to fix this program.
One would see you having to work out the order yourself, and do each Print Name() separately.
The other method uses a single command so that the computer does all the hard work.